
HOME < Technology < DMVPN Introduction
1. What’s DMVPN?
Dynamic Multipoint Virtual Private Network (DMVPN) is a solution which enables the data to transfer from one site to another, without having the verification process of traffic. we can use to build a VPN network with multiple sites without having to statically configure all devices. It’s a Hub and Spoke network where the spokes will be able to communicate with each other directly without having to go through the hub. Encryption is supported through IPSec which makes DMVPN a popular choice for connecting different sites using regular Internet connections.
2. DMVPN Advantages
Simplified hub router configuration - No more multiple tunnel interfaces for each branch (spoke) VPN. A single mGRE and IPSec tunnel configuration is all that requires regardless the number of spoke routers.
Spoke routers can use dynamic (not static) IP Addresses - only the hub router needs to have a publicly-reachable IP address.
Dynamic creation of spoke-to-spoke VPN tunnels - Spoke routers can dynamically create VPN tunnels between them if network data needs to travel from one branch to another (DMVPN Phase 2 with appropriate routing configuration only).
IPSec can be configured to provide data confidentiality and integrity for mGRE traffic.
Traffic between remote sites does not need to traverse the hub (headquarter VPN router).
Reduces the cost of secure communications and connections between branches by integrating VPN with communication practices
DMVPN deployment eliminates additional bandwidth requirements at the hub.
DMVPNs eliminate additional network delays.
DMVPNs conserve WAN bandwidth.
Increase resiliency and redundancy.
3. DMVPN Components
MGRE (Multipoint GRE) a single GRE interface that can secure several IPsec tunnels, reducing the overall scope of the DMVPN configuration
NHRP (Next Hop Resolution Protocol) is the catalyst which facilitates dynamic tunnel establishment, providing tunnel-to-physical interface address resolution. NHRP clients (spoke routers) issue requests to the next hop server (hub router) to obtain the physical address of another spoke router.
One router acts as the NHRP server.
The rest routers act as NHRP clients.
NHRP clients register with the NHRP server and report their public IP addresses.
The NHRP server keeps track of all public IP addresses in its cache.
When router A wants to tunnel something to router B, it will request router B’s public IP address from the NHRP server.
Routing Protocol allows the DMVPN to find routes between different endpoints much more effectively.
IPSec VPN meaning that static crypto maps between individual IPsec tunnel endpoints do not have to be configured.
4. DMVPN Phases
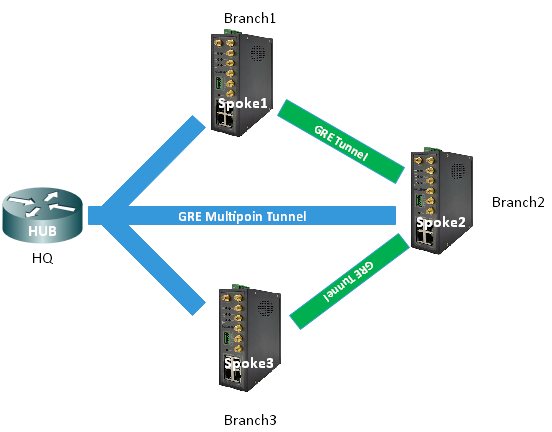
There are three distinct phrases of DMVPN design.
DMVPN Phase1 uses HUB-and-spoke tunnel architecture. The tunnels through which inter-branch connections are made are only built through the central DMVPN hub and the individual spokes. All traffic flows from spokes to and through the hub.
DMPVN Phase 2 uses spoke-to-spoke tunnel deployment, allows spoke-to-spoke tunnels based on demand and triggers, meaning that data doesn’t have to travel to the central hub first, along as there are specific routes in place for the spoke subnets.
DMPVN Phase 3 allows for spoke-to-spoke tunnel architecture, but without the specific pre-made routes in place, but rather uses NHRP traffic indication messages from the hub to secure those routes on the fly.
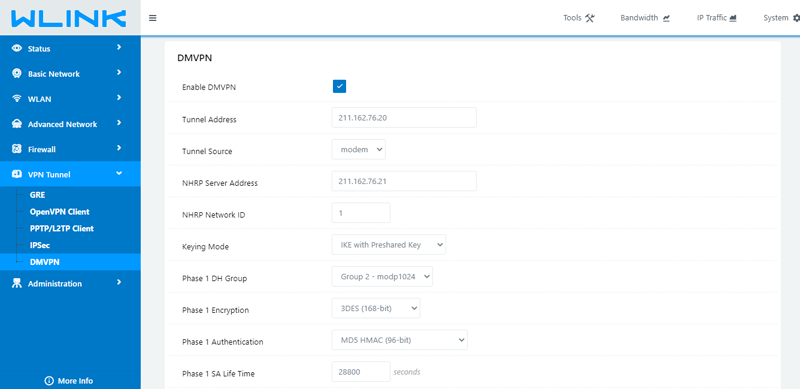
5. DMVPN in WLINK 5G Router
---End











