
HOME < Technology < Create VLAN in Wlink Router
1. Introduction
The Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) is a network technology used to logically separate large broadcast domains using layer 2 devices. VLAN is a logical group of workstations, servers and network devices that appear to be on the same LAN despite their geographical distribution. VLAN allows the computers and users of network to communicate in a simulated environment as if they exist in a single LAN, and are sharing a single broadcast and multicast domain.
VLANs are implemented to achieve scalability, security and ease of network management and can quickly adapt to changes in network requirements and relocation of workstations and server nodes.
2. VLAN Protocol
VLAN tags for Ethernet networks follow the IEEE 802.1Q industry standard. An 802.1Q tag consists of 32 bits (4 bytes) of data inserted into the Ethernet frame header. The first 16 bits of this field contain the hardcoded number 0x8100 that triggers Ethernet devices to recognize the frame as belonging to an 802.1Q VLAN. The last 12 bits of this field contain the VLAN ID number from 1 to 4094.
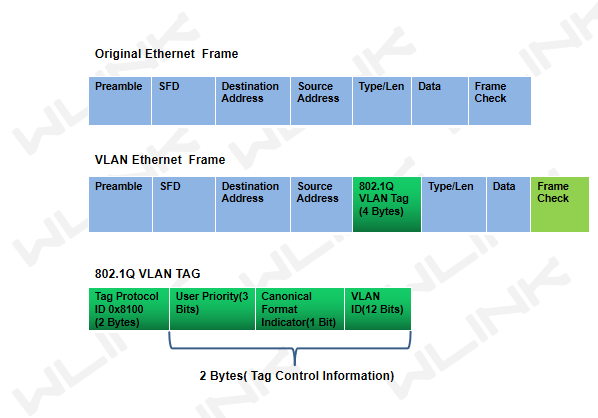
802.1Q Tag fields as following.
Tag Protocol (2 Bytes) is globally and always have a value of 0x8100 to signify an 802.1Q tag.
User Priority (3 Bits) is used by 802.1Q to implement Layer 2 quality of service (QoS).
Canonical Format Indicator (1 Bit) is used for compatibility purposes between Ethernet and Token Ring.
VLAN ID (12 bits) is used to distinguish VLANs on the link.
3. VLAN Categories
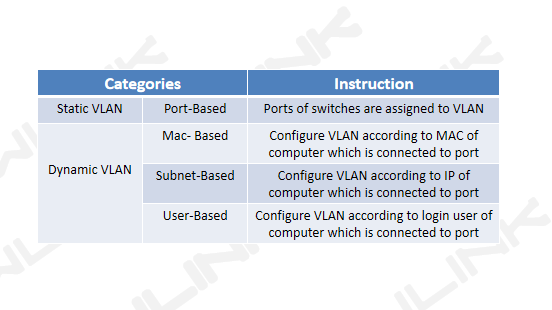
4. When to use VLANs
The PC1 needs to communicate with the PC3 in two Layer 2 switches network as the following figure. The data frame must be specified the destination MAC address to communicate, so the PC1 must first broadcast the "ARP Request" message to try to obtain the MAC address of the PC3. The ARP request will be forwarded to all PCs in the same network. It will be generated network storms to cause network congestion and security issue.
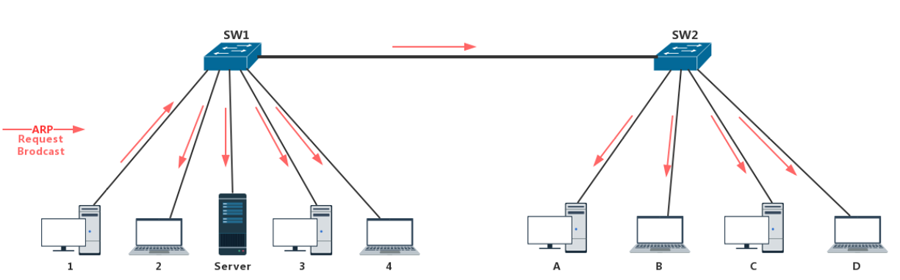
What can we do to improve this situation? VLAN is the economic and secure solution.
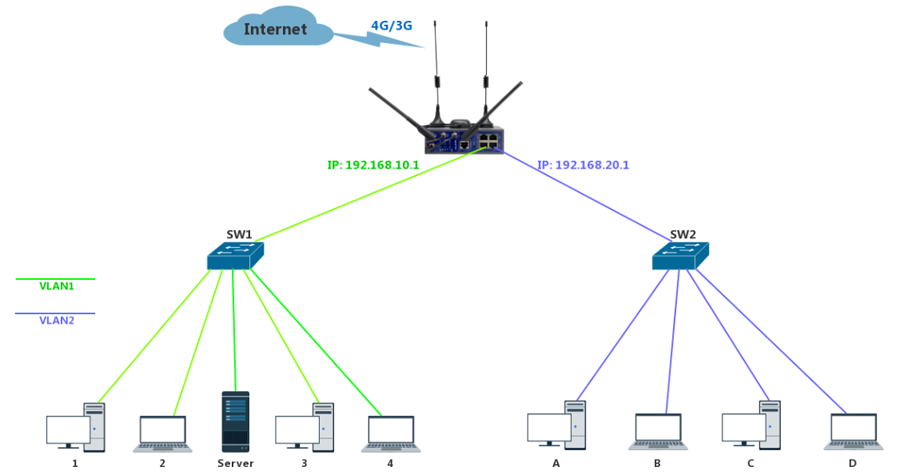
Below is a simple instance to create VLAN on WLINK WL-G510 to explain.
The switch will only forward it to other ports that belong to VLAN1, and will not forward it to the ports belong to VLAN2 after sent a broadcast from PC1.
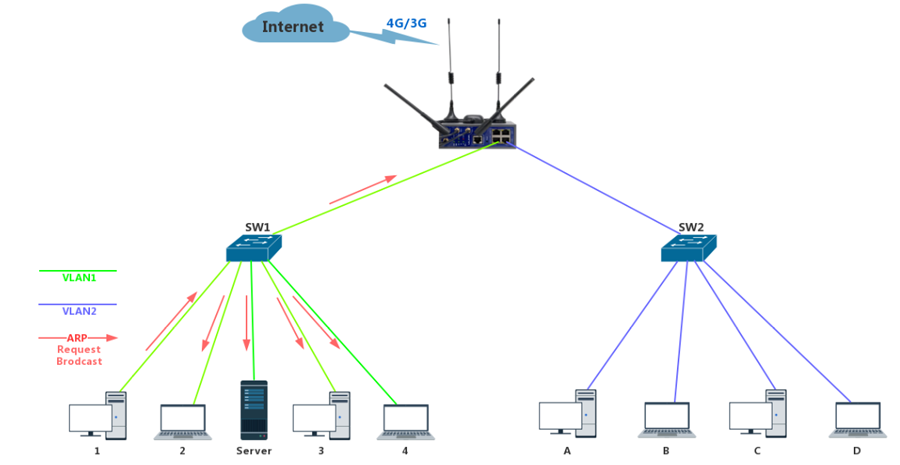
5. Why VLAN
5.1 Improved security
VLANs provide enhanced network security. In a VLAN network environment, with multiple broadcast domains, network administrators have control over each port and user. A malicious user can no longer just plug their workstation into any switch port and sniff the network traffic using a packet sniffer. The network administrator controls each port and whatever resources it is allowed to use.
5.2 Higher performance
Dividing the network into different virtual sub-networks reduces unnecessary traffic and improves performance. Decreasing the latency and traffic load on the network and the network devices, offering increased performance.
5.3 Cost reduction
Segmenting a large VLAN to smaller VLANs is cheaper than creating a routed network with routers because normally routers costlier than switches.
5.4 Simplified network management
Providing flexibility because administrators are able to configure in a centralized environment while the devices might be located in different geographical locations.
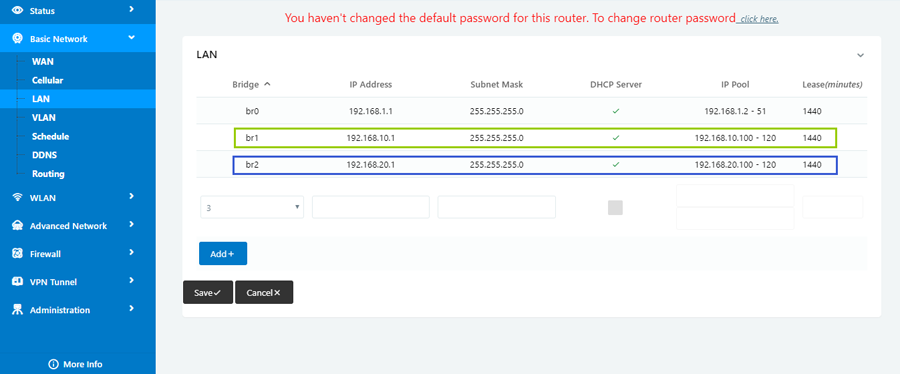
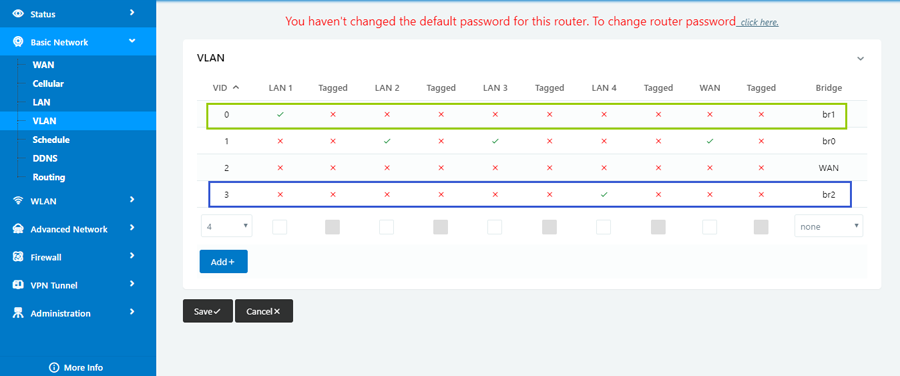
6. VLANs in WL-G510 Series Router
WL-G510 supports VLAN partition based on Ethernet port (LAN1~LAN4)
--THE END











