
HOME < Technology < OSPF Protocol
1. Overview
The OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) protocol is one of a family of IP Routing protocols, and is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) for the Internet, used to distribute IP routing information throughout a single Autonomous System (AS) in an IP network. The OSPF protocol is a link-state routing protocol, which means that the routers exchange topology information with their nearest neighbors. The topology information is flooded throughout the AS, so that every router within the AS has a complete picture of the topology of the AS. Therefore, the next hop address to which data is forwarded is determined by choosing the best end-to-end path to the eventual destination in a link-state routing protocol.
2. How OSPF works
Two neighboring routers become neighbors by sending messages, and then neighbors send link status information each other to form adjacency relation. Then they calculate routing according to the shortest path algorithm and put routing in OSPF routing table. OSPF routing will be added to the global routing table after compared with other routings. The OSPF operation process as following.
1) Learn itself links
Each router learn itself links which it is directly connected network.
2) Search neighbors
OSPF does not immediately broadcast routing information to the network after run. but first looks for the peripheral routers which can exchange link status information each other in the network. Routers are neighboring which can exchange link status information each other.
3) Create link status packets
Once the router establishes a neighbor relationship, it can create link state packets.
4) Link status information transfer
The router will flood the LSA of link state to neighbor, and finally form the link state database containing the complete link state information of the network.
5) Calculate routing
Each router in the routing area can use SPF algorithm to independently calculate the routing
3. OSPF Packet Header
All OSPFv2 packets have a common 24-byte header, and OSPFv3 packets have a common 16-byte header, that contains all information necessary to determine whether OSPF should accept the packet. The header consists of the following fields.
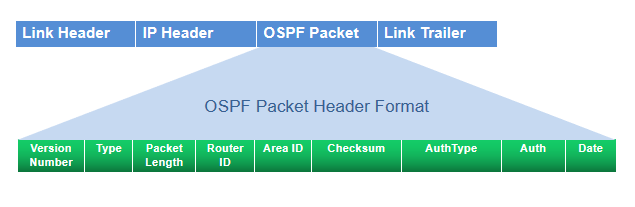
1) Version number
The current OSPF version number. It can be either 2 or 3.
2) Type
Type of OSPF packet.
3)Packet length
Length of the packet, in bytes, including the header.
4) Router ID
IP address of the router from which the packet originated.
5) Area ID
Identifier of the area in which the packet is traveling. Each OSPF packet is associated with a single area. Packets traveling over a virtual link are labeled with the backbone area ID, 0.0.0.0. .
6) Checksum
Fletcher checksum.
7) Auth-Type
Authentication type includes non-Authentication, Simple (text) password, MD5 which value are for 0,1,2 respectively.
8) Authentication (OSPFv2 only)
Authentication scheme and authentication information.
9) Instance ID (OSPFv3 only)
Identifier used when there are multiple OSPFv3 realms configured on a link.
4.OSPF Messages
OSPF uses certain messages for the communication between the routers operating OSPF.
1) Hello message
These are keep alive messages used for neighbor discovery /recovery. These are exchanged in every 10 seconds. This include following information : Router I’d, Hello/dead interval, Area I’d, Router priority, DR and BDR IP address, authentication data.
2) Database Description (DBD)
It is the OSPF routes of the router. This contains topology of an AS or an area (routing domain).
3) Link State Request (LSR)
When a router receive DBD, it compares it with its own DBD. If the DBD received has some more updates than its own DBD then LSR is being sent to its neighbor.
4) Link State Update (LSU)
When a router receives LSR, it responds with LSU message containing the details requested.
Link state acknowledgement. This provides reliability to the link state exchange process. It is sent as the acknowledgement of LSU.
5) Link State Advertisement (LSA)
It is an OSPF data packet that contains link-state routing information, shared only with the routers to which adjacency has been formed.
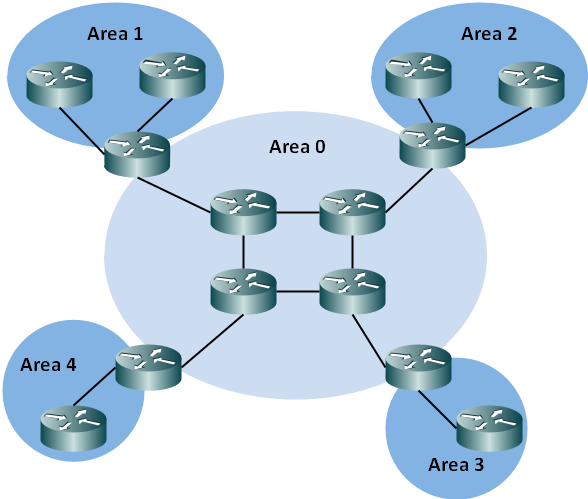
5. OSPF Areas
An OSPF network can be divided into areas that are logical groupings of hosts and networks. An area includes its connecting router having interfaces connected to the network. Each area maintains a separate link state database whose information may be summarized towards the rest of the network by the connecting router. Areas are uniquely identified with 32-bit numbers. The area identifiers are commonly written in the dot-decimal notation, familiar from IPv4 addressing. However, they are not IP addresses and may duplicate, without conflict, any IPv4 address. The area identifiers for IPv6 implementations (OSPFv3) also use 32-bit identifiers written in the same notation.
OSPF uses areas to simplify administration and optimize traffic and resource utilization. An area is simply a logical grouping of contiguous networks and routers. All routers in the same area have the same topology table and don’t know about routers in the other areas. The main purpose of using areas in an OSPF network are.
1) The routing tables on the routers are reduced.
2) Less time is required to run the SFP algorithm, since routers need to recalculate their link-state database only when there’s a topology change within their own area.
3) Routing updates are reduced.
6. OSPF Advantage
1) OSPF is a true LOOP- FREE (route-free loop) routing protocol. It is derived from the merits of the algorithm itself.
2) Fast convergence of OSPF. The route changes can be transmitted to the entire autonomous system in the shortest time.
3) The concept of area division is proposed. After the autonomous system is divided into different regions, the summary of routing information between the regions is adopted, which greatly reduces the quantity of routing information to be transmitted. It also makes routing information not expand rapidly as the network scale increases.
4) The protocol itself minimizes the overhead.
5) Through the strict division of the level of routing (a total of four points), it provides more reliable routing.
6) Good security. OSPF supports interface-based plaintext and md5 authentication.
7) OSPF adapts to various scales of networks, up to thousands of units.
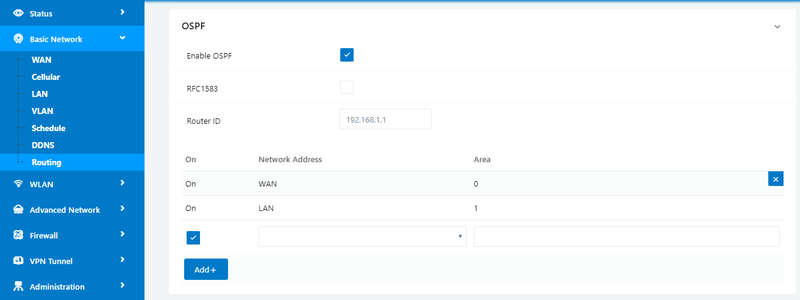
7. OSPF In WLINK 4G/4G+ Router
-- The End











