
HOME < Technology < M2M and IoT
Internet of Things
A “thing” is any object with embedded electronics that can transfer data over a network — without any human interaction.
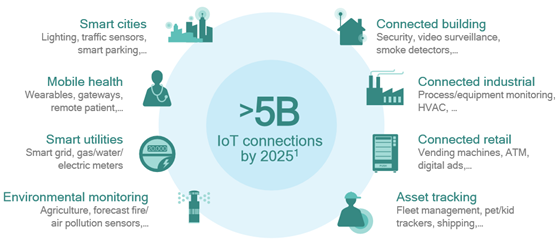
Cellular technologies enable a wide range of IoT services:
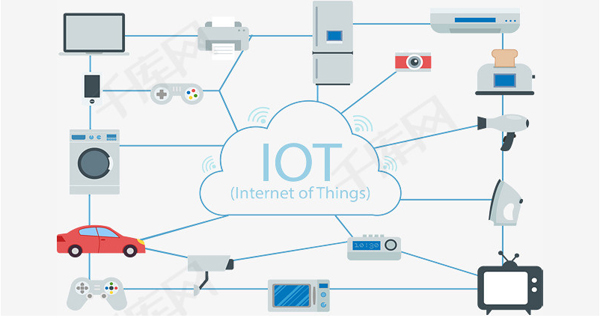
IOT (Internet of things) concept is proposed in 1999, it is very simple definition: all items are connected through radio frequency identification and other information sensing equipment with the Internet, to achieve intelligent identification and management. The IOT refers to the integration of various information sensing devices, such as radio frequency identification (RFID) devices, infrared sensors, global positioning systems, laser scanners. The formation of a huge network, is "all the network." IOT is a network, rather than the final terminal of the object, we talk about things more than the terminal in the past, such as RFID, some sensors, meters. The development trend of IOT at present, requiring the network not only to receive information, but also to send information, the use of more real-time open network, it Need a lot of security mechanisms to ensure the safety of the network, so the essence of IOT is the network.
M2M
Machine to machine (M2M) is a broad label that can be used to describe any technology that enables networked devices to exchange information and perform actions without the manual assistance of humans.
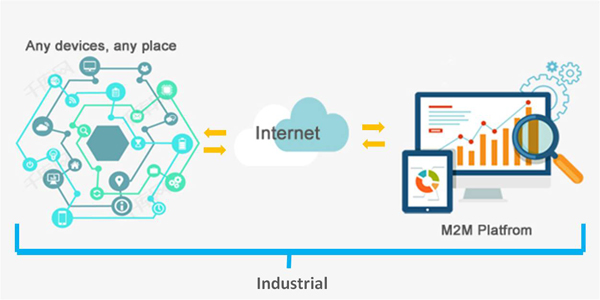
M2M communication is often used for remote monitoring. In product restocking, for example, a vending machine can message the distributor when a particular item is running low. M2M communication is an important aspect of management, remote control, robotics, traffic control, logistic services, supply chain management, fleet management and telemedicine. It forms the basis for a concept known as the Internet of Things(IoT).
What is the difference between IoT and M2M?
First of all, we can be certain that these two concepts do indeed have different meanings. Most conclude that Internet of Things is a broader concept, which will evolve from M2M and other technologies.
For example, traditional M2M solutions typically rely on point-to-point communications using embedded hardware modules and either cellular or wired networks. In contrast, IoT solutions rely on IP-based networks to interface device data to a cloud or middleware platform.
Simply put, Machine-to-Machine is where “Machines” use network resources to communicate with remote application infrastructure for the purposes of monitoring and control, either of the “machine” itself, or the surrounding environment. The potential interconnection of smart objects and the way we interact with the environment is what The Internet of Things is envisioned to be, where the physical world will merge with the digital world.
M2M is what provides The Internet of Things with the connectivity that enables capabilities, which would not be possible without it.
M2M with Internet protocols could be considered a subset of the Internet of Things and understood from a more vertical and closed point of view. On the other hand, the Internet of Things encompasses a more horizontal and meaningful approach where vertical applications are pulled together to address the needs of many people.
By comparing the situation of IOT and M2M, M2M can only be seen as part of the IOT, is a subset of IOT. Only when the M2M scale, universal, and between each other through the network to achieve intelligent integration and communication, to form a "Internet of Things." So, the little bit of the isolated M2M is not the IOT, but the ultimate goal of M2M is the Internet of Things. To achieve the real IOT, it needs massive addresses, massive bandwidth, mass storage, and high communication intelligence and management intelligence, also need a very good regulatory regulations to ensure the viability of the business, these are the current technical capacity and level can not be achieved, so the real realization of IOT can only be carried out in the future.
How M2M & IoT will change our life
People continue to flock to cities for several reasons, such as employment opportunities, lifestyle, and more.
As this migration continues, cities will need to become more efficient in order to keep up with the surging population. Thus, smart cities will start to become the norm in the major metropolitan areas of the world.
But what is a smart city?
Quite simply, smart cities use Internet of Things (IoT) & M2M devices such as connected sensors, lights, and meters to collect and analyze data. The cities then use this data to improve infrastructure, public utilities and services, and more.
Below, we've outlined how smart cities provide a more efficient and higher quality lifestyle for their residents.
Homes
Perhaps the typical example of the Internet of Things is the 'smart home'. The components include sensor-equipped white goods, security, lighting, heating, ventilation and entertainment devices, among others, all connected to a local server or gateway, which can be accessed by the appropriate service providers.
Healthcare
Healthcare is another excellent M2M application. Patients can be issued with sensors (e.g. for blood pressure, or blood sugar levels), sent home and monitored remotely by medical staff — and can often be shown how to interpret the data themselves. This will free up hospital beds and physicians' time for more urgent cases.
Buildings
The smart home is a subset of the 'smart building' — which could be an office, a hotel, a hospital, a manufacturing facility, a retail store or any other public structure. All such buildings consume energy through heating, ventilation and air-conditioning systems, and building automation systems can capture and analyse data from all relevant equipment, allowing cost-saving energy solutions to be created and implemented. Depending on the particular building, other subsystems that can be 'smartened' include structural health, access control and security, lighting, water, lifts, fire and smoke alarms, power and cooling for IT infrastructure.
Automotive & transport
Today's cars routinely bristle with sensors and computing equipment, covering everything from engine management to navigation to 'infotainment'. Automobiles are rapidly becoming connected, context-aware machines that know where they are, where other vehicles are, who is driving (via driver face recognition) and how they are driving, and can warn of impending mechanical or other problems, and automatically summon roadside assistance or emergency services if necessary. A 'smart' car can be remotely tracked or immobilized if stolen.
Retail
The sharp end of the supply chain — retail — is fertile ground for M2M technology, applying to areas such as in-store product placement and replacement, vending machine management, parking meters and wireless payment systems.
Field service
Consumer devices, business equipment and industrial plants can all, obviously, suffer faults that require repairing. If these things are all 'smart', delivering real-time status feedbacks to the internet, then field-service operations can be booked quicker, engineers can be equipped with the correct parts and manuals, and site visits can be scheduled efficiently.
What role does WLINK cellular equipment play in M2M system and IoT network?
As we know various of "Machine" are distributed throughout anywhere on the earth. Traditionally, the network relied on cable Fiber/ADSL to provide network connectivity for sending message and connecting to the server centre, say the connection between machine and machine is via cable network. However, there are quite a large number of location lacking wired coverage condition or it is expensive and difficult to deploy wire network infrastructure.
That is why we need a mobile cellular device in the system, obviously, the main role for WLINK cellular equipment is Provide reliable mobile network connection for machine-to-machine communication and data transmission, as the bridge of interconnection. Small partial of a M2M whole system, however, so important it is.











